Configure User Impersonation
PaletteAI supports Kubernetes User Impersonation. User impersonation is a feature that allows a user to impersonate another user. This is useful for scenarios where you are unable to configure the Kubernetes API server to trust the Dex as an OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider. Through the user impersonation feature, you can continue to use your existing OIDC provider or local Dex users, the key part is to ensure that proper group mappings are configured so that the user has the correct permissions to access the resources they need.
If you configured your Kubernetes API server to trust Dex as an OIDC provider, do not enable user impersonation. The User impersonation feature will not use the JWT token returned from Dex to when authenticating with the Kubernetes API server but instead will use a service account token and apply the impersonation headers to the request.
Overview
To better understand how user impersonation works, review the following diagram.
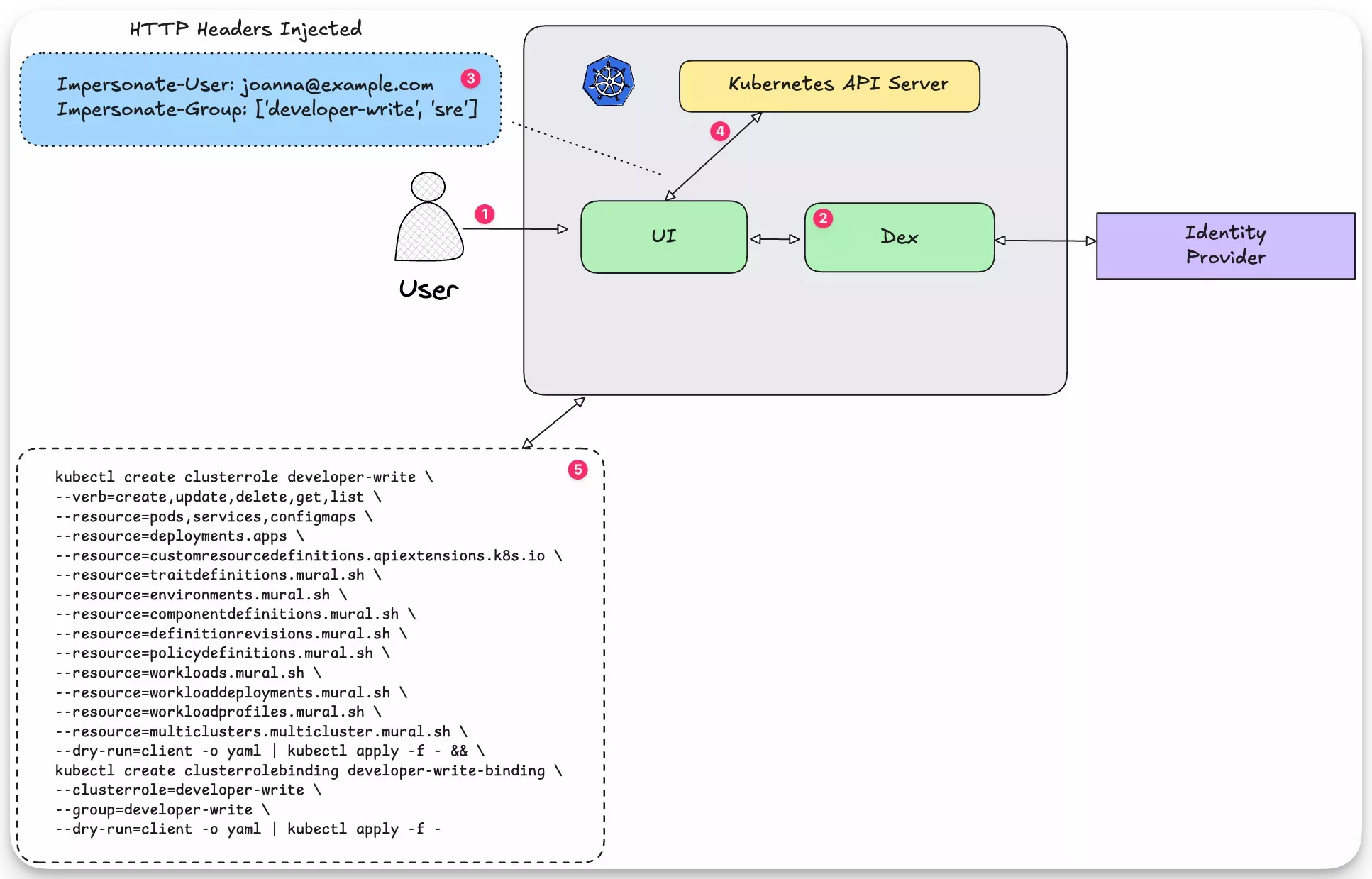
- A user logs in to PaletteAI.
- The PaletteAI UI redirects the user to Dex and the user authenticates with the OIDC provider. If no OIDC provider is configured, the user authenticates with the as a local Dex user using their username and password.
- The user is redirected back to PaletteAI and the user is now authenticated. When the user invokes an action that requires interaction with the Kubernetes API server, PaletteAI adds the user and group impersonation headers to the HTTP request.
- The Kubernetes API reviews the request against configured RBAC rules and grants access to the requested resources if the user has the necessary permissions.
- The user is granted access as they are tied to the
developer-writegroup that has a role binding to thedeveloper-writerole. Without this role binding, the user would not be able to access the requested resources.
Impersonation headers must be added to all HTTP requests to the Kubernetes API server.
Impersonate-User: joanna@example.com
Impersonate-Group: developer-write
Impersonate-Group: sre
When using the PaletteAI UI and user impersonation is enabled, PaletteAI will automatically add the impersonation headers to the HTTP request. However, the PaletteAI administrator must properly configure the group mappings to ensure that the users have the correct permissions to access the resources they need.
User impersonation works outside the PaletteAI UI as well. For example, if you are using the kubectl CLI, you add the --as and --as-group flags to the command to impersonate a user. Below is an example of how to use the kubectl CLI to impersonate a user using the fictional user joanna@example.com and the developer-write group.
kubectl --as=joanna@example.com --as-group=developer-write get componentdefinitions --namespace PaletteAI-system
To use kubectl with user impersonation, you need to ensure that the kubectl CLI is configured to use Dex as the OIDC provider. Review the Configure Kubernetes API Server to Trust OIDC Provider guide and the steps starting at ten to learn how to configure the kubectl CLI to use Dex as the OIDC provider.
Enable and Configure User Impersonation
User impersonation is disabled by default in PaletteAI. To enable user impersonation, update the PaletteAI values.yaml file to set the canvas.impersonationProxy.enabled flag to true.
canvas:
impersonationProxy:
enabled: true
You can trigger the update through either the helm upgrade command. Or by updating the canvas-config secret in the PaletteAI-system namespace. If you update the canvas-config secret, the Canvas server will automatically restart, and the new configuration will take effect.
Configure User Impersonation
The user impersonation feature is configured in the canvas.impersonationProxy section of the PaletteAI values.yaml file. The following parameters are available:
| Parameter | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
enabled | Whether to enable user impersonation. | false |
userMode | The mode to use for user impersonation. The userMap specifies a 1:1 mapping between external users, such as local Dex users or OIDC users, to Kubernetes users. If userMode is map, it is used to identify values for Impersonate-User headers. If userMode is passthrough, the Impersonate-User header automatically uses the current user's email address as the value. Valid options are map or passthrough. | passthrough |
groupsMode | The groupsMode maps external groups to Kubernetes groups. If external groups match Kubernetes groups, use passthrough and do not define a groupMap. Otherwise, use map and define your groupMap. Valid options are passthrough or map. | passthrough |
userMap | If userMode is map, the provided mapping is used to identify values for Impersonate-User headers. For example "bob@example.com": "bob@kubernetes.com". This is only used for mapping external users to an actual Kubernetes user. The syntax is <external-user>: <'local-kubernetes-user'> | {} |
groupMap | The groupMap maps external groups to Kubernetes groups. Each external group may translate to one or more Kubernetes groups. Values can be a list of Kubernetes groups. An Impersonate-Group header will be added for every Kubernetes group associated with an external user. For example "groups-in-azure": ["k8s-devs", "k8s-sre"]. Not applicable to local Dex users. Local Dex users can be mapped to Kubernetes groups using the dexGroupMap parameter. The syntax is <external-group>: ['<kubernetes-group-name>']. | {} |
dexGroupMap | The dexGroupMap maps local Dex users to Kubernetes groups. Each Dex user may translate to one or more Kubernetes groups. An Impersonate-Group header will be added for every Kubernetes group associated with a Dex user. Dex does not support groups for local Dex users, you can use this to overcome the Dex limitation. Requires groupsMode to be set to map. For example "admin@example.com": ["k8s-admin", "k8s-superadmin"]. | {} |
Common Scenarios
The following are some common scenarios for configuring user impersonation.
In the PaletteAI UI, visit the /whoami to review detailed authentication information about the current user. Information such as groups, API permissions, and applied impersonationProxy settings can be found in the page. Use this to debug access issues and to verify that the user access is configured correctly.
In all the following example scenarios, it's assumed the proper cluster role and role binding are configured to grant the user the necessary permissions to access the requested resources.
Map Local Dex Users to Kubernetes Groups
If you are using local Dex users, you can map them to Kubernetes groups using the dexGroupMap parameter. This is useful if you are using local Dex users and you want to map them to Kubernetes groups.
In the following example, the admin@example.com user is mapped to a Kubernetes admin group. The guest@example.com user is mapped to the Kubernetes developer-write and developer-read groups.
canvas:
impersonationProxy:
enabled: true,
userMode: 'passthrough',
groupsMode: 'map',
userMap: {},
groupMap: {},
dexGroupMap:
'admin@example.com': [ 'admin' ]
'guest@example.com': ['developer-write', 'developer-read']
As the user guest@example.com logs into PaletteAI, the Impersonate-User header will be set to guest@example.com and the Impersonate-Group header will be set to developer-write and developer-read.
Impersonate-User: guest@example.com
Impersonate-Group: developer-write
Impersonate-Group: developer-read
If you don't want to map each user to a Kubernetes group, consider configuring an OIDC provider in Dex vs using local Dex users. Using an OIDC provider through Dex avoids the need to map each user to a Kubernetes group.
Map OIDC Groups to Kubernetes Groups
Another scenario is to map OIDC groups to Kubernetes groups. When an OIDC provider is configured in Dex, the user's groups are returned in the JWT token. You can use the groupMap parameter to map the OIDC groups to Kubernetes groups.
canvas:
impersonationProxy:
enabled: true,
userMode: 'passthrough',
groupsMode: 'map',
userMap: {},
groupMap:
admin: 'developer-write'
backup: 'k8s-backup'
developer: ['developer-read', 'k8s-backup']
dexGroupMap: {}
Assume an example scenario where the user admin@example.com logs into PaletteAI and is a member of the admin and backup groups and the JWT token contains the following groups:
{
"groups": ["admin", "backup"]
}
The Impersonate-Group header will be set to developer-write and k8s-backup as the mapping is defined in the configuration and the user is a member of the admin and backup groups.
Impersonate-User: admin@example.com
Impersonate-Group: developer-write
Impersonate-Group: k8s-backup
Map an OIDC User to a Kubernetes User
You can map an OIDC user to a Kubernetes user using the userMap parameter. Kubernetes users not to be confused with local Dex users. A Kubernetes user is created by presenting a certificate signed by the cluster's Certificate Authority (CA) to the Kubernetes API server and deriving the name from the Common Name (CN) in the certificate. Check out the Users in Kubernetes page to learn more about Kubernetes users. Acquiring the cluster's CA is not always available in all Kubernetes clusters, such as managed Kubernetes clusters.
If you are in a scenario where you want to use Kubernetes users, you can map an OIDC user to a Kubernetes user by setting the userMode to map and the userMap to the OIDC user. In the following example, the OIDC user joanna@example.com is mapped to the Kubernetes user joanna@kubernetes.com. Similar to the Map OIDC Groups to Kubernetes Groups scenario, assume the JWT returned from Dex will contain the admin and backup groups. In this example, the user joanna@example.com is a member of the admin group.
canvas:
impersonationProxy:
enabled: true,
userMode: 'map',
groupsMode: 'map',
userMap:
"joanna@example.com": "joanna@kubernetes.com"
groupMap:
admin: "developer-write"
backup: "k8s-backup"
dexGroupMap: {}
The Impersonate-User header will be set to joanna@kubernetes.com and the Impersonate-Group header will be set to developer-write and k8s-backup as the mapping is defined in the configuration and the user is a member of the admin group.
Impersonate-User: joanna@kubernetes.com
Impersonate-Group: developer-write
Map a Local Dex User to a Kubernetes User
You can map local Dex users to Kubernetes users using the userMap parameter. In the following example, the local Dex user joanna@example.com is mapped to the Kubernetes user joanna@kubernetes.com. Because joanna@example.com is a local Dex user, the dexGroupMap parameter is used to map the user to the Kubernetes developer-write group. The userMap ensures that the Impersonate-User header is set to joanna@kubernetes.com.
canvas:
impersonationProxy:
enabled: true,
userMode: 'map',
groupsMode: 'map',
userMap:
"joanna@example.com": "joanna@kubernetes.com"
groupMap: {},
dexGroupMap:
"joanna@example.com": ["developer-write"]
The HTTP headers will be set to the following values:
Impersonate-User: joanna@kubernetes.com
Impersonate-Group: developer-write