Configure Kubernetes API Server to Trust OIDC Provider
The Kubernetes API server can be configured to trust an OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider to authenticate users. We recommend you work with your Kubernetes administrator and security team to configure the Kubernetes API server to trust the OIDC provider. Depending on your infrastructure provider and the Kubernetes platform you are using, such as AWS EKS, Azure AKS, or Google GKE, the steps to configure the Kubernetes API server to trust the OIDC provider may vary.
To help you configure the Kubernetes API server to trust the OIDC provider, below is a list of links to configuration guides for some common Kubernetes platforms.
OIDC Configuration Prerequisites
- Administrator access to the Kubernetes API server.
- You need network access to the following systems:
- The Kubernetes API server.
- The OIDC provider.
- The Kubernetes API server must have network access to the OIDC provider.
- You must have the following information available from the OIDC provider:
- Issuer URL.
- Username claim, typically
emailorsub. - Groups claim, typically
groups. - Username prefix.
It's possible your OIDC provider has additional configuration requirements and may require additional information that is not listed in the prerequisites. Review the Kubernetes API server OIDC options documentation for an exhaustive list of configuration options.
Configure the Kubernetes API Server to Trust the OIDC Provider
Use the following guide to experiment with configuring a Kind cluster to trust the Dex instance deployed by PaletteAI. You can use the same concept to experiment with configuring a production Kubernetes cluster to trust your own OIDC provider.
Prerequisites
- Install Kind v0.27.0 or greater.
- Download and install ngrok.
- Once
ngrokis installed, complete the post-installation instructions for logging in and configuring yourauthtoken.
- Once
- Install kubectl v1.30 or greater.
- Install Kubelogin v1.31 or greater to use the OIDC login command. If you are using a Kubernetes plugin manager, such as
krew, make sure to update the plugin to the latest version through the plugin manager. You can check the version you have installed by issuingkubectl oidc-login version.
Setup
-
Create a directory for the demo setup.
mkdir -p paletteai-oidc-demo/ssl && cd paletteai-oidc-demo -
Use
ngrokto open a secure Agent tunnel between your local machine and dynamic endpoint provided byngrok.ngrok http https://localhost:5554An Agent tunnel summary will appear in your terminal that displays your dynamic endpoint. In this example it is
https://4464-72-217-54-22.ngrok-free.app, but you will get a different value.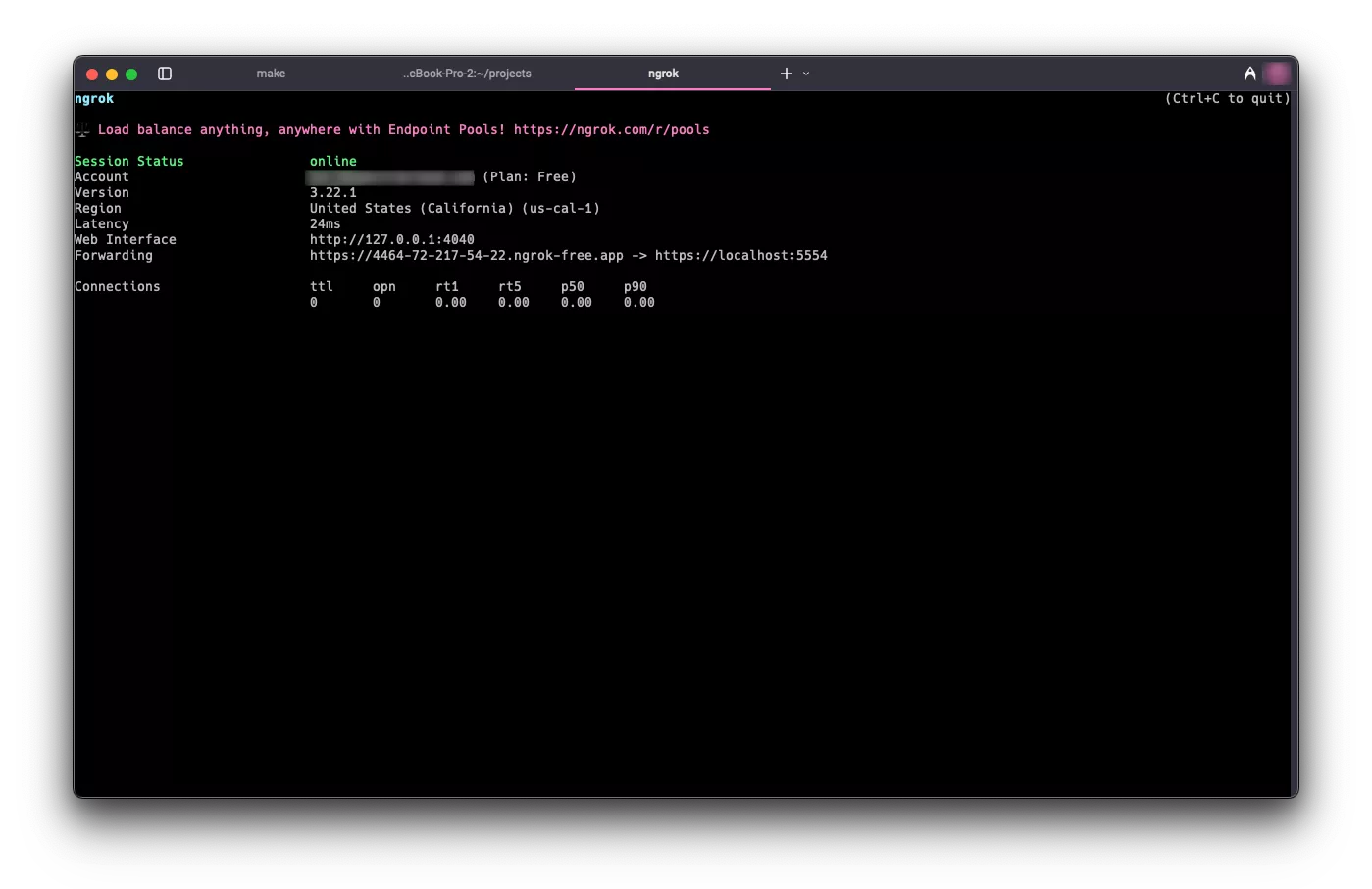
Copy it and export it as an environment variable by issuing the following command.
export NGROK_ENDPOINT=<your_ngrok_endpoint> -
Next, issue the following command to create a
kind-config.yamlfile with some Kubernetes API server configuration. Take note of theapiServer.extraArgssection. This section is used to configure the Kubernetes API server to trust the OIDC provider. Theoidc-issuer-urlis configured to use thengrokendpoint you configured in the previous step.cat <<EOF > kind-config.yaml
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
networking:
apiServerAddress: '127.0.0.1'
apiServerPort: 6443
nodes:
- role: control-plane
kubeadmConfigPatches:
- |
kind: ClusterConfiguration
apiServer:
extraArgs:
oidc-issuer-url: $NGROK_ENDPOINT
oidc-client-id: kubernetes
oidc-username-claim: email
oidc-username-prefix: ""
oidc-groups-claim: groups
EOF -
Create the Kind cluster.
kind create cluster --name dev --kubeconfig $HOME/dev.kubeconfig --config kind-config.yamlCreating cluster "dev" ...
✓ Ensuring node image (kindest/node:v1.32.2) 🖼
✓ Preparing nodes 📦
✓ Writing configuration 📜
✓ Starting control-plane 🕹️
✓ Installing CNI 🔌
✓ Installing StorageClass 💾
Set kubectl context to "kind-dev"
You can now use your cluster with:
kubectl cluster-info --context kind-dev --kubeconfig /Users/demo/dev.kubeconfig
Have a nice day! 👋 -
Set the kubectl context to the newly created cluster.
export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/dev.kubeconfig -
Issue the following command to create a
values.yamlfile that contains Dex configurations. The important configuration is thestaticClientssection. This section defines a client for the Kubernetes API server to authenticate with. Theidwith the namekubernetesis the name of the client. This is the same value that you placed in theoidc-client-idfield in thekind-config.yamlfile. The configuration below is also creating a static password for theadmin@example.comuser. The password is hashed using bcrypt with the valuepassword.cat <<EOF > values.yaml
dex:
enabled: true
replicaCount: 1
commonLabels: {}
image:
repository: ghcr.io/dexidp/dex
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
tag: ''
digest: ''
imagePullSecrets: []
namespaceOverride: ''
nameOverride: ''
fullnameOverride: 'dex'
hostAliases: []
https:
enabled: true
configSecret:
create: true
name: ''
config:
issuer: $NGROK_ENDPOINT
logger:
level: debug
format: text
storage:
type: kubernetes
config:
inCluster: true
web:
http: 0.0.0.0:5556
https: 0.0.0.0:5554
tlsCert: /etc/k8s-webhook-certs/tls.crt
tlsKey: /etc/k8s-webhook-certs/tls.key
grpc:
addr: 0.0.0.0:5557
tlsCert: /etc/k8s-webhook-certs/tls.crt
tlsKey: /etc/k8s-webhook-certs/tls.key
tlsClientCA: /etc/k8s-webhook-certs/ca.crt
telemetry:
http: 0.0.0.0:5558
enablePasswordDB: true
oauth2:
passwordConnector: local
staticClients:
- id: kubernetes
redirectURIs:
- https://dex.mural.local/callback
- 'http://localhost:8000'
name: kubernetes
secret: iamasecret
public: false
staticPasswords:
- email: 'admin@example.com'
hash: '\$2a\$12\$Ot2dJ0pmdIC2oXUDW/Ez1OIfhkSzLZIbsumsxkByuU3CUr02DtiC.'
username: 'admin'
userID: '08a8684b-db88-4b73-90a9-3cd1661f5466'
expiry:
idToken: '8h'
volumes:
- name: tls-cert-vol
secret:
secretName: mural-dex-serving-cert
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/k8s-webhook-certs
name: tls-cert-vol
readOnly: true
envFrom: []
env: {}
envVars: []
serviceAccount:
create: true
annotations: {}
name: ''
rbac:
create: true
createClusterScoped: true
deploymentAnnotations: {}
deploymentLabels: {}
podAnnotations: {}
podLabels: {}
podDisruptionBudget:
enabled: false
minAvailable:
maxUnavailable:
priorityClassName: ''
podSecurityContext: {}
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
securityContext: {}
service:
annotations: {}
type: ClusterIP
clusterIP: ''
loadBalancerIP: ''
ports:
http:
port: 5556
nodePort:
https:
port: 5554
nodePort:
grpc:
port: 5557
nodePort:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: 'nginx'
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: mural
hosts:
- host: dex.mural.com
paths:
- path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
tls:
- hosts:
- dex.mural.local
secretName: mural-dex-serving-cert
serviceMonitor:
enabled: false
namespace: ''
interval:
scrapeTimeout:
labels: {}
annotations: {}
scheme: ''
path: /metrics
tlsConfig: {}
bearerTokenFile:
honorLabels: false
metricRelabelings: []
resources: {}
autoscaling:
enabled: false
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 100
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 80
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
topologySpreadConstraints: []
strategy: {}
networkPolicy:
enabled: false
EOFClick to learn more about the default configuration YAML file
There are a few important things to note about the default
values.yamlfile and the Dex configuration.The first value to note is the
issuervalue. This is the URL Dex will use to issue tokens and inject into the JWT token as theissvalue. The value is set to thengrokendpoint in this example. In production, theissuervalue must match the domain you assign to PaletteAI.Next, the
staticClientssection defines a client. From Dex's perspective, a client is any application or resource that will request a token from it. In this case, the client is the Kubernetes API server. Theidwith the valuekubernetesis the client's name. This is the same value you placed in theoidc-client-idfield in thekind-config.yamlfile. When the Kubernetes API server requests Dex to validate a JWT token, it will include the client IDkubernetesin the request, and Dex, in return, will use the configurations provided in thestaticClientssection to validate the token along with expected claims and secrets. This configuration also includes a redirect URL ofhttp://localhost:8000. This value was added to allow Kubelogin to authenticate with the Dex. Kubelogin by default uses the URLhttp://localhost:8000as the redirect URL.Lastly, the
staticPasswordssection defines a password for a static user,admin@example.com. The password is hashed using bcrypt with the valuepassword. Dex supports local users, but be aware that this is not a recommended practice. Local users are limited in functionality and cannot be assigned a group. In production, we recommend managing users with an external identity provider. -
Use the PaletteAI helm chart to install Dex. All other PaletteAI components are intentionally disabled to keep the focus on the Dex configuration.
helm install mural oci://public.ecr.aws/mural/mural:0.6.2 \
--namespace mural-system --create-namespace --values values.yaml --set=canvas.enabled=false --set=cert-manager.enabled=true --set=flux2.enabled=false --set=hue.enabled=false --set=fleetConfig.enabled=false --set=fleetconfig-controller.enabled=false --set=ingress-nginx.enabled=true --set=brush.enabled=false --set=zot.enabled=false --set=alertmanager.enabled=false --set=fluxcd-manager.enabled=false -
Wait for the Dex pod to be ready.
kubectl wait --for=condition=ready pod --selector app.kubernetes.io/name=dex --namespace mural-system --timeout=120s -
Expose the Dex service by setting up a port forward.
kubectl port-forward service/dex 5554:5554 --namespace mural-system >/dev/null 2>&1 & -
Configure your kubeconfig file to use the OIDC provider.
kubectl oidc-login setup \
--oidc-issuer-url=$NGROK_ENDPOINT \
--oidc-client-id=kubernetes \
--oidc-client-secret=iamasecret \
--oidc-extra-scope=email -
A browser window will open up and take you to the Dex login page. Use the
admin@example.comuser and the password valuepassword.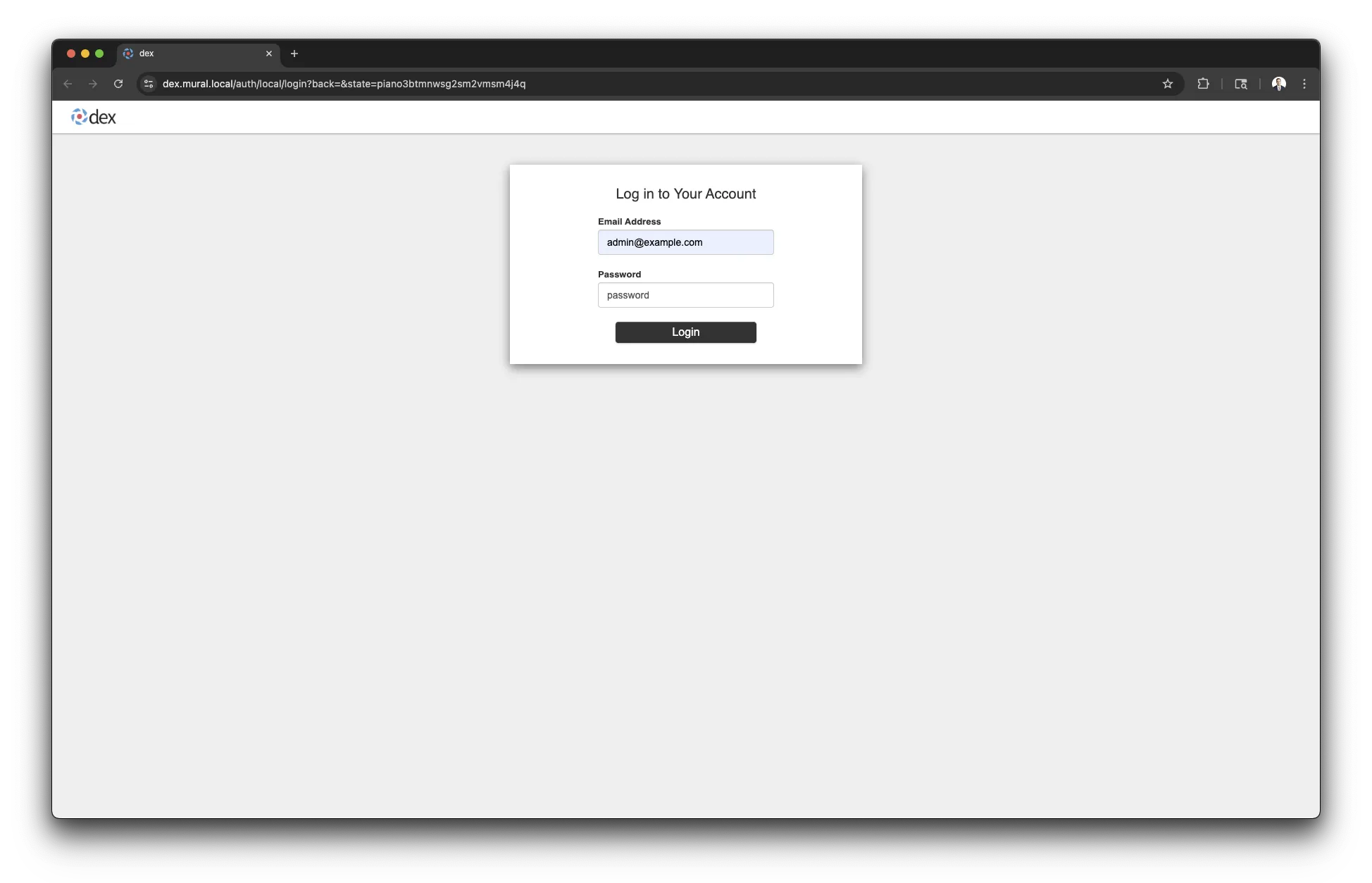
Upon successful login, you will receive a token and commands to setup a kubeconfig file.
Authentication in progress...
## Authenticated with the OpenID Connect Provider
You got the token with the following claims:
{
"iss": "https://4464-72-217-54-22.ngrok-free.app",
"sub": "CiQwOGE4Njg0Yi1kYjg4LTRiNzMtOTBhOS0zY2QxNjYxZjU0NjYSBWxvY2Fs",
"aud": "kubernetes",
"exp": 1747928601,
"iat": 1747842201,
"nonce": "cd5zFM0VCCIUa4RA1Phcfpl4mBC9Tfbl1pawD2dCWRk",
"at_hash": "WrpeK3mWeNLwWlGEer3ZfA",
"c_hash": "DdnjC7om5Ajo02Owjxva4Q",
"email": "admin@example.com",
"email_verified": true
}
... -
Navigate back to the terminal. Issue the
kubectl config set-credentialscommand to create a user namedoidc.kubectl config set-credentials oidc \
--exec-api-version=client.authentication.k8s.io/v1 \
--exec-command=kubectl \
--exec-arg=oidc-login \
--exec-arg=get-token \
--exec-arg=--oidc-issuer-url=$NGROK_ENDPOINT \
--exec-arg=--oidc-client-id=kubernetes \
--exec-arg=--oidc-client-secret=iamasecret \
--exec-arg=--oidc-extra-scope=email \
--exec-arg=--token-cache-dir=$HOME/.kube/cache/oidc \
--exec-interactive-mode=Always -
Create a role binding that grants the new user access to the cluster. Otherwise, the new user will not be able to perform any actions.
kubectl create clusterrolebinding oidc-admin-binding \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--user=admin@example.com -
Change the current context to the new OIDC user.
kubectl config use-context kind-dev --user=oidc -
Switch to the new user.
kubectl config set-context --current --user=oidc
Validate
Use the following command to verify the new OIDC user has access to the cluster.
-
Issue the following command to verify you are the new user.
kubectl config view --minify --output jsonpath='{.users[0].name}'tipIf you have gone through the setup before, make sure to clear the token cache for the OIDC user. Otherwise, a stale token may result in an unauthorized error.
rm -rfv $HOME/.kube/cache/oidc -
Issue the following command to verify the new user has access to the cluster. A browser window will open up and take you to the Dex login page. Use the
admin@example.comuser and the actual password to authenticate.kubectl get pods --all-namespacesYou should receive an output similar to the following.
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-668d6bf9bc-fmch5 1/1 Running 0 7m22s
kube-system coredns-668d6bf9bc-s6k55 1/1 Running 0 7m22s
kube-system etcd-canvas-dev-control-plane 1/1 Running 0 7m28s
kube-system kindnet-72rph 1/1 Running 0 7m22s
kube-system kube-apiserver-canvas-dev-control-plane 1/1 Running 0 7m28s
kube-system kube-controller-manager-canvas-dev-control-plane 1/1 Running 0 7m28s
kube-system kube-proxy-p8z67 1/1 Running 0 7m22s
kube-system kube-scheduler-canvas-dev-control-plane 1/1 Running 0 7m28s
local-path-storage local-path-provisioner-7dc846544d-j6vz9 1/1 Running 0 7m22s
mural-system cert-manager-cainjector-5c87f4477-rmwvw 1/1 Running 0 6m45s
mural-system cert-manager-fd6dcf8cb-45v8s 1/1 Running 0 6m45s
mural-system cert-manager-webhook-54cd859596-shwtq 1/1 Running 0 6m45s
mural-system dex-6dc95f9d7f-2mqpn 1/1 Running 0 6m45s
mural-system helm-controller-69b7c9dbd7-pg5zw 1/1 Running 0 6m45s
mural-system kustomize-controller-657f4fdfcd-5bqll 1/1 Running 0 6m45s
mural-system source-controller-5dc6d5d47-r9nll 1/1 Running 0 6m45s
Next Steps
Now that you have a local kind cluster configured to trust Dex as an OIDC provider and have observed the workflow, you can experiment with configuring a new kind cluster to trust your own OIDC provider.
You should also practice configuring Dex to use your OIDC provider as a connector. Check out the Dex Connectors documentation for information on how to configure different OIDC providers.
To authenticate users with the PaletteAI UI, you must configure the following:
- Kubernetes must trust Dex as an OIDC provider
- Dex must use an OIDC provider connector configured for your OIDC provider
As you make changes to the Dex configuration, you can use the following command to update Helm release.
helm upgrade mural oci://public.ecr.aws/mural/mural:0.6.2 \
--namespace mural-system --values values.yaml --set=canvas.enabled=false --set=cert-manager.enabled=true --set=flux2.enabled=false --set=hue.enabled=false --set=fleetConfig.enabled=false --set=fleetconfig-controller.enabled=false --set=ingress-nginx.enabled=true --set=brush.enabled=false --set=zot.enabled=false
Once you are done experimenting, you can delete the kind cluster with the following command.
kind delete cluster --name dev